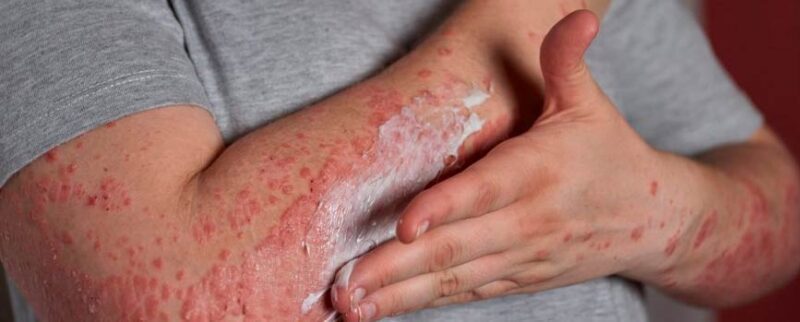
Unmasking the Culprits: A Comprehensive Guide to Types of Skin Fungi
Skin fungal infections are a common ailment affecting millions worldwide. Understanding the different types of skin fungi is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This guide delves into the most prevalent types of skin fungi, their symptoms, causes, and available treatments. By familiarizing yourself with these fungal foes, you can better protect your skin and maintain optimal health.
What are Skin Fungi?
Types of skin fungi are microorganisms that thrive on the surface of the skin, hair, and nails. These fungi, also known as dermatophytes, feed on keratin, a protein that makes up these structures. While some fungi are harmless, others can cause infections, leading to various skin conditions.
Common Types of Skin Fungi Infections
Several types of skin fungi can cause infections. Here are some of the most common:
Tinea Infections
Tinea is a general term for fungal infections of the skin. The specific type of tinea is determined by the location of the infection. These infections are highly contagious and spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or by touching contaminated objects.
- Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot): This infection affects the feet, particularly between the toes. Symptoms include itching, burning, scaling, and cracked skin. [See also: Athlete’s Foot Prevention Tips]
- Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch): This infection affects the groin area, causing itching, redness, and a rash. It is more common in men and is often associated with sweating and tight clothing.
- Tinea Corporis (Ringworm): This infection can occur on any part of the body, causing a circular, raised, and scaly rash that resembles a ring. It is highly contagious and can be spread through contact with infected animals or surfaces.
- Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm): This infection affects the scalp and hair follicles, causing scaling, itching, and hair loss. It is more common in children.
- Tinea Unguium (Onychomycosis): Also known as nail fungus, this infection affects the nails, causing them to become thick, discolored, and brittle. It can be difficult to treat and may require oral medication.
Yeast Infections
Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of yeast, a type of fungus that is naturally present on the skin. The most common type of yeast infection is caused by Candida species, particularly Candida albicans.
- Cutaneous Candidiasis: This infection affects the skin, particularly in warm, moist areas such as the armpits, groin, and between the fingers and toes. Symptoms include redness, itching, and a rash.
- Oral Thrush: This infection affects the mouth and throat, causing white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks. It is more common in infants, elderly individuals, and people with weakened immune systems.
- Vaginal Yeast Infection: This infection affects the vagina, causing itching, burning, and a thick, white discharge. It is very common in women.
Pityriasis Versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is a fungal infection caused by Malassezia, a type of yeast that is normally present on the skin. The infection causes small, discolored patches to appear on the skin, typically on the chest, back, and upper arms. These patches may be lighter or darker than the surrounding skin and may become more noticeable after sun exposure. This type of skin fungi is not contagious.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing types of skin fungi infections. These include:
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or diabetes, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Warm and Moist Environment: Fungi thrive in warm and moist environments. Sweating, wearing tight clothing, and living in humid climates can increase the risk of infection.
- Poor Hygiene: Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing regularly or sharing personal items, can increase the risk of infection.
- Contact with Infected Individuals or Animals: Direct contact with infected individuals or animals can spread fungal infections.
- Use of Antibiotics: Antibiotics can kill beneficial bacteria that help to control fungal growth, increasing the risk of yeast infections.
Diagnosis
A doctor can usually diagnose a skin fungal infection by examining the affected area. In some cases, a skin scraping or a sample of the infected nail may be taken and sent to a laboratory for testing to identify the specific type of skin fungi causing the infection. This is particularly important for nail infections, as they can be caused by different types of fungi and require specific treatments.
Treatment Options
Treatment for skin fungal infections depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common treatment options include:
- Topical Antifungal Medications: These medications are applied directly to the affected area. They are effective for treating mild to moderate fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm. Common topical antifungal medications include clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: These medications are taken by mouth and are used to treat more severe or widespread fungal infections, such as nail fungus and scalp ringworm. Common oral antifungal medications include terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole. These medications can have side effects and should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
- Antifungal Shampoos: These shampoos are used to treat scalp ringworm and other fungal infections of the scalp. They contain antifungal ingredients such as ketoconazole or selenium sulfide.
- Home Remedies: Some home remedies, such as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, and garlic, may help to relieve the symptoms of mild fungal infections. However, it is important to consult with a doctor before using home remedies, as they may not be effective for all types of fungal infections.
Prevention
Preventing types of skin fungi infections involves practicing good hygiene and avoiding risk factors. Here are some tips to help prevent fungal infections:
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Wash regularly with soap and water, and dry thoroughly, especially in areas where sweat accumulates.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing: Avoid wearing tight clothing, which can trap moisture and create a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Wear Moisture-Wicking Fabrics: Choose fabrics that wick away moisture, such as cotton or synthetic blends.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, socks, shoes, or other personal items.
- Wear Sandals in Public Showers and Locker Rooms: Protect your feet from fungal infections by wearing sandals in public showers and locker rooms.
- Treat Existing Infections Promptly: If you develop a fungal infection, treat it promptly to prevent it from spreading to other parts of your body or to other people.
- Maintain a Healthy Immune System: Eat a healthy diet, get enough sleep, and manage stress to maintain a healthy immune system.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to see a doctor if you suspect you have a skin fungal infection, especially if:
- The infection is severe or widespread.
- The infection does not improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- You have a weakened immune system.
- You have diabetes.
- You are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of skin fungi and their associated infections is essential for effective prevention and treatment. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding risk factors, and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary, you can protect your skin and maintain optimal health. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and ensuring a speedy recovery from types of skin fungi infections. Consulting with a healthcare professional is always recommended for personalized advice and treatment options. Identifying the specific type of skin fungi is key to effective treatment. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, but professional medical advice should always be sought.
The world of types of skin fungi can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and preventative measures, you can keep your skin healthy and fungus-free. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your skin health!
