Drone Geofencing Technology: A Comprehensive Guide to Safety, Security, and Compliance
Drone technology has revolutionized various industries, from agriculture and construction to surveillance and delivery services. However, the increasing use of drones also presents safety and security challenges. One crucial technology addressing these concerns is drone geofencing technology. This article provides a comprehensive overview of drone geofencing technology, exploring its functionalities, applications, benefits, and the critical role it plays in ensuring responsible drone operations.
What is Drone Geofencing Technology?
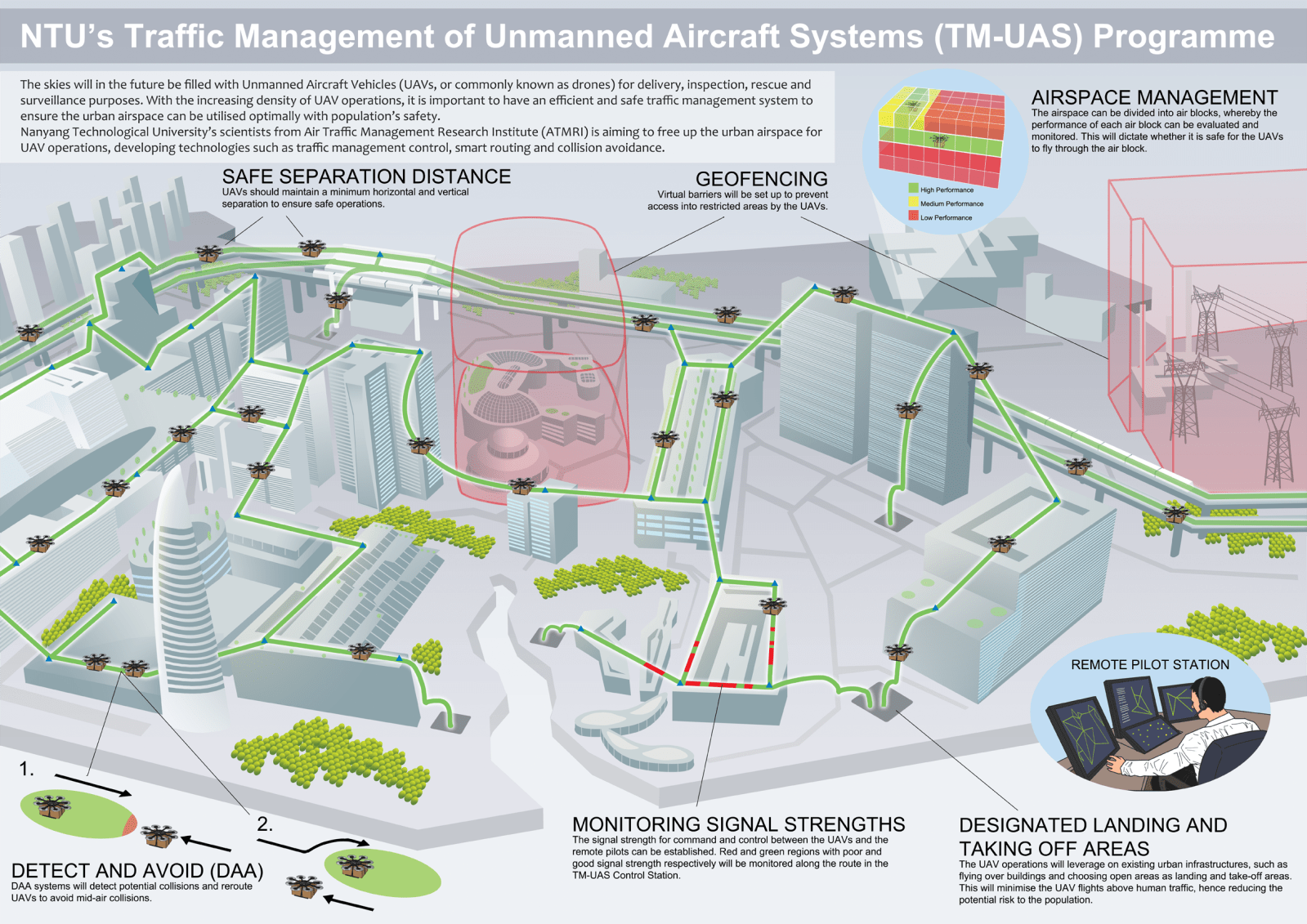
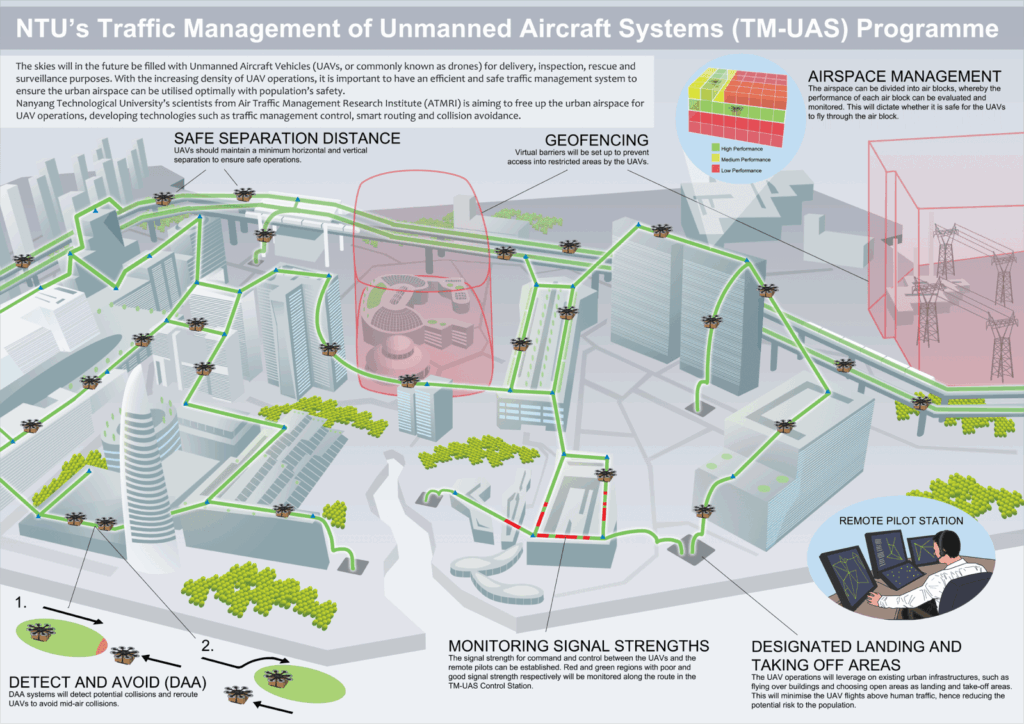
Drone geofencing technology utilizes GPS or other positioning systems to create virtual boundaries around specific geographic areas. These boundaries, known as geofences, act as invisible barriers for drones. When a drone approaches or crosses a geofence, the system triggers a pre-defined action, such as preventing the drone from entering the area, alerting the operator, or automatically returning the drone to its launch point. This technology is crucial for maintaining safety, security, and regulatory compliance in drone operations.
How Drone Geofencing Works
The functionality of drone geofencing technology can be broken down into several key components:
- GPS/Positioning System: Drones use GPS or other positioning systems like GLONASS or Galileo to determine their precise location in real-time.
- Geofence Definition: Geofences are defined as virtual perimeters, typically using mapping software or drone control applications. These perimeters can be simple shapes like circles or rectangles, or complex polygons to match specific geographic features.
- Real-time Monitoring: The drone’s onboard computer constantly monitors its position relative to the defined geofences.
- Action Triggering: When the drone violates a geofence, the system triggers a pre-programmed action. This could include:
- Prevention: Preventing the drone from entering the restricted area.
- Alerting: Sending notifications to the drone operator or a central monitoring system.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically initiating the drone’s return-to-home function.
- Landing: Forcing the drone to land immediately.
Key Benefits of Drone Geofencing Technology
Implementing drone geofencing technology offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: Preventing drones from entering restricted airspace, such as airports or critical infrastructure, significantly reduces the risk of accidents and collisions.
- Improved Security: Geofencing can protect sensitive areas, such as prisons or government buildings, from unauthorized drone flights. This helps prevent espionage, smuggling, and other security threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many countries and regions have regulations restricting drone flights near airports, populated areas, and other sensitive locations. Drone geofencing technology helps operators comply with these regulations, avoiding fines and legal penalties.
- Operational Control: Geofencing allows operators to define safe operating zones for their drones, ensuring they stay within designated areas and avoid potential hazards. This is particularly useful for commercial drone operations, such as inspections or deliveries.
- Reduced Liability: By implementing geofencing, drone operators can demonstrate a commitment to safety and responsible operation, potentially reducing their liability in case of accidents or incidents.
Applications of Drone Geofencing
The applications of drone geofencing technology are diverse and span numerous industries:
- Airport Protection: Geofencing is crucial for preventing drones from entering airport airspace, protecting aircraft and ensuring passenger safety.
- Critical Infrastructure Security: Protecting power plants, oil refineries, and other critical infrastructure from drone-related threats.
- Law Enforcement: Establishing geofences around crime scenes or public events to prevent unauthorized drone surveillance.
- Event Management: Defining no-fly zones around crowded events to ensure public safety.
- Construction Sites: Preventing drones from entering construction zones to avoid accidents and protect workers.
- Agricultural Applications: Defining boundaries for crop spraying or monitoring activities.
- Delivery Services: Restricting drone deliveries to specific areas and routes.
Types of Geofences
Geofences can be categorized based on their characteristics and functionality:
- Static Geofences: These are pre-defined boundaries that remain fixed unless manually updated. They are suitable for protecting permanent locations, such as airports or power plants.
- Dynamic Geofences: These boundaries can be adjusted in real-time based on changing conditions, such as weather patterns or temporary restrictions. They are useful for managing drone operations in dynamic environments.
- Reactive Geofences: These are triggered by specific events, such as a drone approaching a restricted area. They are used to provide immediate alerts or take corrective actions.
Implementing Drone Geofencing: Key Considerations
Successfully implementing drone geofencing technology requires careful planning and consideration:
- Accuracy: Ensure the GPS or positioning system provides accurate location data to avoid false alarms or missed violations.
- Reliability: The geofencing system should be reliable and robust, able to withstand interference or disruptions.
- Customization: The system should allow for customization of geofence parameters and action triggers to meet specific operational needs.
- Integration: The geofencing system should be seamlessly integrated with the drone’s flight control system and other relevant software applications.
- Testing: Thoroughly test the geofencing system in various scenarios to ensure it functions correctly and effectively.
- Regular Updates: Keep the geofence data updated to reflect changes in regulations or geographic features.
Challenges and Limitations
While drone geofencing technology offers significant benefits, it also faces certain challenges and limitations:
- GPS Signal Interference: GPS signals can be affected by interference from buildings, trees, or other obstacles, potentially leading to inaccurate location data and geofence violations.
- Software Glitches: Software bugs or glitches can cause the geofencing system to malfunction, resulting in unintended consequences.
- Operator Override: Some geofencing systems allow operators to override the geofence, potentially compromising safety or security.
- Unauthorized Modifications: Hackers or malicious actors could potentially modify the geofencing system to bypass restrictions or gain unauthorized access to restricted areas.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining a sophisticated drone geofencing technology system can be expensive, particularly for small businesses or individual drone operators.
The Future of Drone Geofencing
The future of drone geofencing technology is promising, with ongoing advancements in positioning systems, sensor technology, and artificial intelligence. These advancements will lead to more accurate, reliable, and sophisticated geofencing systems. Some potential future developments include:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Integration of advanced positioning systems, such as Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS, will improve the accuracy of geofencing systems.
- AI-Powered Geofencing: Artificial intelligence algorithms can be used to dynamically adjust geofences based on real-time conditions, such as weather patterns or traffic congestion.
- Collaborative Geofencing: Geofencing systems could be integrated with other drone management systems, allowing for collaborative control and coordination of drone operations.
- Detect and Avoid Systems: Integration with detect and avoid systems will allow drones to automatically avoid obstacles within or near geofenced areas, further enhancing safety.
- Standardization: Increased standardization of geofencing protocols and data formats will improve interoperability between different drone platforms and management systems.
Conclusion
Drone geofencing technology is a critical component of responsible drone operations. By creating virtual boundaries and enforcing pre-defined actions, geofencing helps ensure safety, security, and regulatory compliance. As drone technology continues to evolve, drone geofencing technology will play an increasingly important role in managing the risks and maximizing the benefits of drones across various industries. Understanding its functionalities, applications, and limitations is essential for drone operators, regulators, and anyone involved in the drone ecosystem. As the technology matures, we can expect even more sophisticated and effective geofencing solutions that contribute to a safer and more secure airspace for everyone.
[See also: Drone Regulations Worldwide]
[See also: Best Drone Safety Practices]
[See also: The Future of Drone Delivery]